
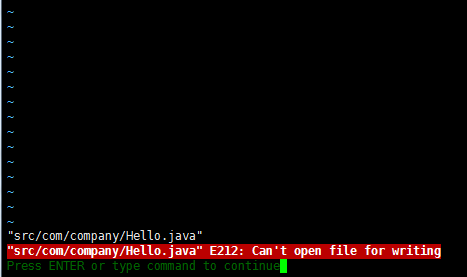
I was trying to edit/create a file in a folder that didn't exist. Don't reload or you'll lose your changes.įor me there was was quite a simple solution. chmod means change permissions, 777 means full permissions everywhere. The bang means start interpreting as shell. You need the exclamation point because you are editing a root file as a lesser user. The permissions are expanded, and the file is saved. Then make some changes to the file, it warns you its read only. One time Setup demo to create a root owned read only file for a lower user: sudo touch temp.txtįirst open the file as normal user: vi temp.txt See this demo of how to save those changes:
Instead of losing all your changes and re-opening with sudo. That happens to me all the time, I open a root file for writing: Or if you don't want to leave your existing vim session (and now have proper sudo rights), you can issue: :w !sudo tee % > /dev/null You might want to edit the file as a superuser as sudo vim FILE. The reason could be that you do not have permission to write in the directory
Join the nixCraft community via RSS Feed, Email Newsletter or follow on Twitter.For some reason the file you are writing to cannot be created or overwritten. He wrote more than 7k+ posts and helped numerous readers to master IT topics. Vivek Gite is the founder of nixCraft, the oldest running blog about Linux and open source. See the following man pages using the man command or help command:

In such case you can save file without login as root using the sudo command. As a sysadmin you might edit a file non-privileged user. You just learned how to save a read-only file edited in vim text editor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
